PyTorch 개념 정리
PyTorch는 메타 AI에서 개발한 파이썬 기반의 오픈 소스 딥러닝 프레임워크로서, 강력한 동적 계산 그래프를 제공하며 연구와 실무에서 널리 사용되고 있습니다. PyTorch의 핵심 개념과 내부 함수들을 살펴봅시다.
1. PyTorch의 주요 특징
PyTorch는 다음과 같은 특징을 가지고 있습니다:
- 동적 계산 그래프(Dynamic Computational Graph): 연산이 정의되는 시점에 그래프가 생성되며, 유연성과 디버깅 용이성을 제공합니다.
- 자동 미분(Autograd): 모든 텐서 연산에 대해 자동으로 그래디언트를 계산할 수 있습니다.
- GPU 가속: 간단한 코드 변경만으로 GPU를 활용할 수 있습니다. nvidia의
cuda를 지원합니다 - 다양한 커뮤니티와 생태계: 풍부한 튜토리얼, 도구 및 모델들이 존재합니다.
계산 그래프란?
계산 그래프(Computation Graph)는 수학적 연산을 노드와 엣지를 이용한 그래프 구조로 표현한 것입니다.
- 노드(Node): 연산(예: 덧셈, 곱셈 등)이나 변수(입력값)를 의미합니다.
- 엣지(Edge): 데이터의 흐름과 의존 관계를 나타냅니다.
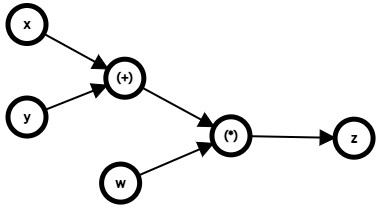
다음과 같은 수식을 가정해봅시다.
\[z = (x+y)\cdot w\]이 수식에 대한 계산 그래프는 다음과 같이 그릴 수 있습니다.
이와 같은 그래프를 통해 모델 학습 시 학습의 흐름을 구조화하고, 미분과 역전파를 효율적으로 계산할 수 있게 해줍니다. 그렇다면 동적 계산 그래프는 무엇일까요?
동적 계산 그래프란?
동적 계산 그래프는 연산을 수행할 때 실시간으로 그래프를 생성하는데, 정적 계산 그래프에서는 모델의 구조를 먼저 정의하고, 이후 입력이 이를 통과하도록 설계됩니다. 반면, 동적 계산 그래프는 코드 실행 중에 그래프가 생성되고 변경됩니다.
동적 방식의 장점:
- 유연성: 계산 그래프가 실시간으로 생성되므로, 복잡한 제어 흐름(예: 조건문, 반복문)도 자연스럽게 처리할 수 있습니다.
- 디버깅 용이성: Python 디버깅 도구를 사용하여 연산을 추적하고 디버깅할 수 있습니다.
- 간소화된 모델 개발: 모델 구조를 실시간으로 변경할 수 있어 실험과 연구에 적합합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
import torch
def dynamic_graph_example(x):
if x > 0:
y = x ** 2
else:
y = x ** 3
return y
x = torch.tensor(2.0, requires_grad=True)
result = dynamic_graph_example(x)
result.backward()
print(x.grad) # x > 0이므로 dy/dx = 2x = 4.0
2. PyTorch의 주요 구성 요소
(1) Tensor
PyTorch의 기본 데이터 구조는 Tensor입니다. NumPy 배열과 유사하게 작동하며 GPU 가속을 지원합니다.
텐서 생성 및 GPU 활용 예제
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
import torch
# 텐서 생성
x = torch.tensor([[1, 2], [3, 4]], dtype=torch.float32)
print("Tensor x:", x) # Tensor x: tensor([[1., 2.], [3., 4.]])
# GPU로 이동
if torch.cuda.is_available():
x_gpu = x.to('cuda')
print("Tensor on GPU:", x_gpu) # Tensor on GPU: tensor([[1., 2.], [3., 4.]], device='cuda:0')
주요 텐서 연산 예제
1
2
3
4
5
6
x = torch.tensor([[1.0, 2.0], [3.0, 4.0]])
print("Sum:", torch.sum(x)) # Sum: tensor(10.)
print("Mean:", torch.mean(x)) # Mean: tensor(2.5)
print("Max:", torch.max(x)) # Max: tensor(4.)
print("Argmax:", torch.argmax(x)) # Argmax: tensor(3)
※PyTorch 텐서는 기본적으로 행렬을 1차원 배열처럼 펼친 순서로 인덱싱합니다.
텐서 변환 및 조작 예제
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
# 텐서 변환
x = torch.tensor([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
# Reshape
reshaped = x.reshape(4, 1)
print("Reshaped Tensor:", reshaped) # Reshaped Tensor: tensor([[1], [2], [3], [4]])
# Transpose
transposed = torch.transpose(x, 0, 1)
print("Transposed Tensor:", transposed) # Transposed Tensor: tensor([[1, 3], [2, 4]])
# Flatten
flattened = torch.flatten(x)
print("Flattened Tensor:", flattened) # Flattened Tensor: tensor([1, 2, 3, 4])
요소 반환 및 계산 함수
1
2
3
4
x = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3, 4, 5], dtype=torch.float32)
print("Max:", torch.max(x)) # Max: tensor(5.)
print("Mean:", torch.mean(x)) # Mean: tensor(3.)
print("Variance:", torch.var(x)) # Variance: tensor(2.5)
텐서 초기화
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
# 특정 값으로 초기화
zeros = torch.zeros((2, 3))
ones = torch.ones((2, 3))
arange_tensor = torch.arange(0, 10, 2)
print("Zeros Tensor:", zeros) # Zeros Tensor: tensor([[0., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 0.]])
print("Ones Tensor:", ones) # Ones Tensor: tensor([[1., 1., 1.], [1., 1., 1.]])
print("Arange Tensor:", arange_tensor) # Arange Tensor: tensor([0, 2, 4, 6, 8])
# 랜덤 값으로 초기화
rand_tensor = torch.rand((2, 3)) # 0과 1 사이의 균등 분포
randn_tensor = torch.randn((2, 3)) # 평균 0, 표준편차 1 정규분포
print("Random Tensor:", rand_tensor) # Random Tensor: tensor([...])
print("Random Normal Tensor:", randn_tensor) # Random Normal Tensor: tensor([...])
(2) Autograd
PyTorch는 자동 미분 기능을 제공합니다. 신경망 학습 과정에서 필수적인 요소입니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
# 자동 미분 예제
x = torch.tensor(2.0, requires_grad=True)
y = x ** 3
y.backward() # y를 x에 대해 미분
print("Gradient:", x.grad) # Gradient: tensor(12.)
(3) Neural Network (nn.Module)
PyTorch에서 신경망은 nn.Module 클래스를 상속하여 정의됩니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
import torch.nn as nn
class SimpleModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(SimpleModel, self).__init__()
self.linear = nn.Linear(2, 1) # 입력 2, 출력 1
def forward(self, x):
return self.linear(x)
# 모델 생성
model = SimpleModel()
x = torch.tensor([[1.0, 2.0]])
output = model(x)
print("Model Output:", output) # Model Output: tensor([[...]], grad_fn=<AddmmBackward0>)
nn.Linear()에 입출력 차원을 지정해주면 해당 차원들에 해당하는 선형변환이 만들어집니다. 이 선형변환에 대한 가중치 행렬의 값은 Kaiming He 초기화(Kaiming Uniform Initialization) 방법을 사용하여 초기화됩니다.
(4) Optimizer
PyTorch는 다양한 최적화 알고리즘을 제공합니다. 가장 널리 사용되는 것은 SGD와 Adam입니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
import torch.optim as optim
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.01)
loss_fn = nn.MSELoss()
y_true = torch.tensor([[5.0]])
for epoch in range(10):
optimizer.zero_grad() # 기울기 초기화
y_pred = model(x) # 예측 값
loss = loss_fn(y_pred, y_true) # 손실 계산
loss.backward() # 역전파
optimizer.step() # 가중치 업데이트
print(f"Epoch {epoch + 1}, Loss: {loss.item()}")
간단하게 파이토치의 개념과 사용법에 대해 알아보았습니다. 해당 포스트에서 언급된 Kaiming He 초기화(Kaiming Uniform Initialization), SGD, Adam 등과 같이 해당 포스트에서 다루지 못한 개념적 내용은 차후 포스트를 통해 더 알아보도록 하겠습니다.